405 results filtered with: Green

- Digital Images
- Online
Artichoke, sagittal view, MRI
Alexandr Khrapichev, University of Oxford
- Digital Images
- Online
Kidney stone
Sergio Bertazzo, Imperial College London; Dominique Bazin, UPMC; Chantal Jouanneau, INSERM.
- Digital Images
- Online
Human oral squamous cell carcinoma cell, SEM
Anne Weston, LRI, CRUK and John Marshall, Tumour Biology Lab
- Digital Images
- Online
Mutant Muscle Sarcomere, Drosophila larva
Hermann Aberle, University of Munster
- Digital Images
- Online
HeLa cells, immortal human epithelial cancer cell line, SEM
Anne Weston, Francis Crick Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Muscle fibres, Drosophila embryo
Hermann Aberle, University of Munster
- Digital Images
- Online
Human heart (mitral valve) tissue displaying calcification
Sergio Bertazzo, Department of Materials, Imperial College London
- Digital Images
- Online
GABAergic and Glutamatergic neurons in the zebrafish brain
Kate Turner, Dr Steve Wilson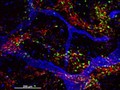
- Digital Images
- Online
Cellular architecture of normal human skin imaged by whole mount tissue microscopy. Human skin has a rich network of white blood cells (specifically dendritic cells, T cells and macrophages) which form sheaths around blood vessels (string-like structures). A network of lymphatic vessels (ribbon-like structures) is also present. In this image, human skin lymphatic vessels (stained for LYVE-1; blue) and white blood cells comprised of dendritic cells (stained for CD11c; green) and T cells (stained for CD3; red) can be seen. Some macrophages also express the protein LYVE-1 similar to lymphatic vessel cells which can be appreciated as blue cells within and in between the sheaths of white blood cells. This normal cellular architecture is grossly disrupted in diseased skin (see related images). X10 magnification. Scale bar (white) represents 200 micrometres.
Dr. Xiao-nong Wang, Human Dendritic Cell Laboratory, Newcastle University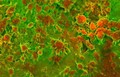
- Digital Images
- Online
Human heart (aorta) tissue displaying calcification
Sergio Bertazzo, Department of Materials, Imperial College London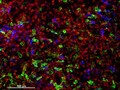
- Digital Images
- Online
Cellular architecture of human skin lymphoma imaged by whole mount tissue microscopy. Normal human skin has a rich network of white blood cells (specifically dendritic cells, T cells and macrophages) which form sheaths around blood vessels. In diseased skin, such as in skin lymphoma as seen here, this normal architecture becomes distorted. In this image, lots of T cells (stained for CD3; red), dendritic cells (stained for CD11c; green) and macrophages (stained for LYVE-1; blue) have infiltrated the skin. X20 magnification. Scale bar (white) represents 100 micrometres.
Dr. Xiao-nong Wang, Human Dendritic Cell Laboratory, Newcastle University
- Digital Images
- Online
Strawberry
Annie Cavanagh
- Digital Images
- Online
Varicose Veins, Legs. Female. Illustrated with thermography
Thermal Vision Research, Wellcome Collection
- Digital Images
- Online
Pinus mugo Turra, Pinaceae Mountain pine. Distribution: Mountain regions in south and central Europe. Source of pine cone syrup used in cooking. Pine trees in general have a small edible pine nut in the pine cone, which Lyte (1578) writes are 'good for the lungs, they cleanse the breast, and cause the fleme to be spit out: also they nourish well and engender good blood, and for this cause they are good for such as have the cough.' He wrote that it was used for burns, wounds, dysentery, and as a diuretic. Quincy says of fir (Pinus) cones that they strengthen the genital parts, and increase the quantity of seed, or increase Desire without adding to Ability or Performance. Photographed in the Medicinal Garden of the Royal College of Physicians, London.
Dr Henry Oakeley
- Digital Images
- Online
Neurones connecting, artwork
Stephen Magrath
- Digital Images
- Online
Neurons or nerve cells are the core components of the brain and spinal cord of the central nervous system (CNS), and of the ganglia of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) controlling many motor and sensory functions of the body.
Odra Noel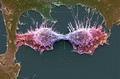
- Digital Images
- Online
HeLa cells, immortal human epithelial cancer cell line, SEM
Anne Weston, Francis Crick Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Raw ginger, illustration
Karen Gustafson
- Digital Images
- Online
Dopaminergic neurons in the zebrafish forebrain. Confocal micrograph of a 4 day old transgenic zebrafish embryo viewed from a lateral aspect. Neurons in the olfactory bulb, telencepahlon, ventral diencephalon, pretectum and hypothalamus are labelled in green. Axonal tracts are shown in cyan and neuropil in magenta. In order to show the anatomy of the brain better the skin and eyes of the embryo have been removed post-fixation.
Kate Turner, Dr Steve Wilson
- Digital Images
- Online
Glycinergic neurons in a zebrafish embryo
Kate Turner, Dr Steve Wilson
- Digital Images
- Online
Rat neurones, SEM
Anne Weston, Francis Crick Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Anaesthesia, artwork
Mary Rouncefield
- Digital Images
- Online
Healthy adult human brain viewed face on, tractography
Henrietta Howells, NatBrainLab
- Digital Images
- Online
Prostate cancer cell, SEM
Anne Weston, Francis Crick Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Group A Streptococci are a species of gram-positive bacteria responsible for causing a number of pyogenic (pus-producing) infections including impetigo, scarlet fever and pneumonia. Further fatal complications arising from infection include the development of meningitis and sepsis.
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute